If you weren’t aware, I’ve been working on a 3D printed 6 axis robot arm since May 2021. You can catch up on all the work I’ve done so far by watching the videos on my YouTube channel, here’s the playlist link
Up until very recently, a good portion of the design process was focused mainly on mechanical design. Now I’ve reached a point where the mechanical design is mostly finalized, I don’t plan on making any major changes unless I’m adding more electronics or sensors to the arm (at least for this version of it). So here’s a quick overview of the mechanical design for those that are curious or looking for inspiration! For a more detailed explanation, check out the YouTube videos!
Overview #

All of the joints are driven using stepper motors, either via direct drive or some sort of reduction. All joints have an endstop that is used to calibrate their respective joints. Almost all of the joints also have an encoder in place for closed-loop control, joints 4 and 6 don’t have an encoder due to design constraints. I may add them later on, and if I do I’ll update this page.
Joint 1 #
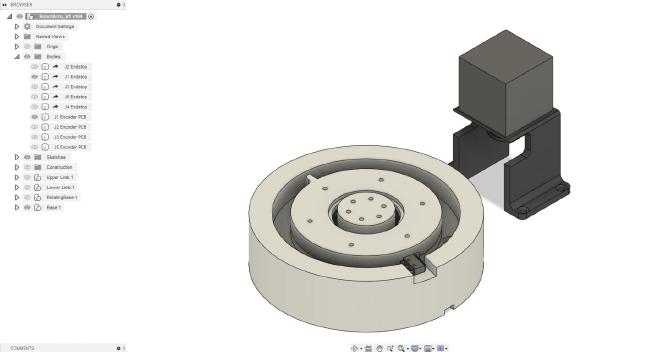
This joint is driven by a 2.8A NEMA 23 stepper motor with a holding torque of 1.26Nm from Stepperonline. The stepper motor output is reduced using a belt drive with a 7:1 reduction ratio. There is an AS5600 encoder at the base of the robot to measure this joint’s angle.
Joint 2 #

This joint is driven by a 4.2A NEMA 23 stepper motor with a holding torque of 3Nm from Stepperonline. The stepper motor output is reduced using a two-stage belt drive with the first stage being a 3:1 and the second stage a 5:1 reduction ratio. There is an AS5600 encoder at the pivot point of this joint to measure its angle.
Joint 3 #

This joint is driven by the same NEMA 23 stepper motor as joint 1 (23HE22-2804S). The stepper motor output is reduced using another two-stage belt drive with the first stage being a 4:1 and the second stage a 5:1 reduction ratio. There is an AS5600 encoder at the pivot point of this joint to measure its angle.
Joint 4 #
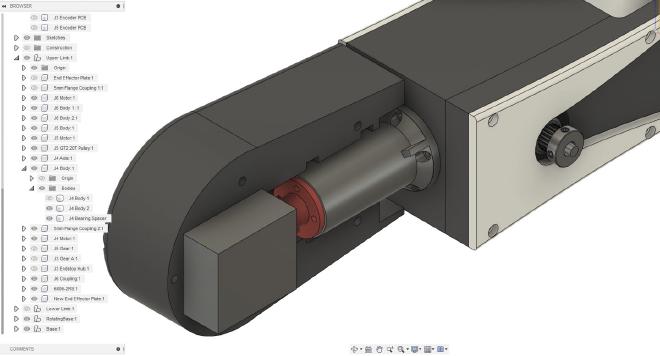
This joint is driven by a 2A NEMA 17 stepper motor with a holding torque of 0.59Nm from Stepperonline. The stepper motor output directly drives this joint. As of right now, there is no encoder to measure this joint’s angle.
Joint 5 #
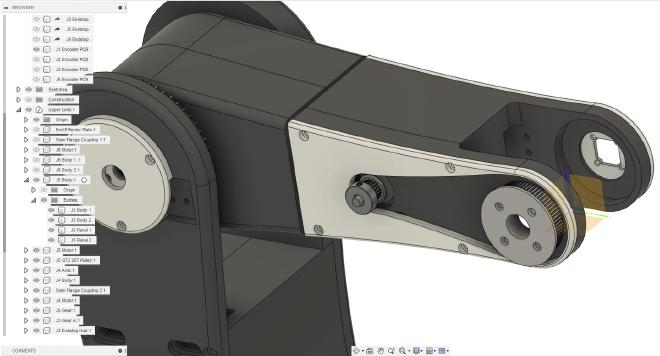
This joint is driven by the same NEMA 17 stepper motor as joint 4 (17HS19-2004S1). The stepper motor output is reduced using a belt drive with a 7:2 (3.5:1) reduction ratio. There is an AS5600 encoder at this joint’s pivot to measure its angle.
Joint 6 #

This joint is driven by a 0.5A NEMA 17 stepper motor with a holding torque of 0.26Nm from Stepperonline. The stepper motor output directly drives this joint. As of right now, there is no encoder to measure this joint’s angle.

